“The Role of Gut Health in Weight Loss.” This timeless quote by Hippocrates underscores the significance of diet in our overall health, including weight loss. Recent studies have highlighted the crucial role of gut health in managing weight.
Table of Contents
ToggleGut health refers to the balance of microorganisms in the digestive tract. A healthy gut microbiome is essential for effective digestion, absorption of nutrients, and regulation of metabolism, all of which impact weight loss. By adopting certain habits and making informed lifestyle choices, individuals can optimize their gut health to support their weight management goals.
Understanding the interplay between gut health and weight loss can empower individuals to make targeted changes, enhancing their overall well-being and improving their chances of successful weight management.
Understanding the Gut-Weight Connection
Recent studies have shed light on the intricate relationship between the gut microbiome and weight regulation. The gut microbiome, comprising trillions of microorganisms, plays a crucial role in our overall health, influencing various physiological processes, including metabolism and weight management.
The Emerging Science of Gut Health
The science of gut health is rapidly evolving, with new discoveries shedding light on how the gut microbiome affects our overall well-being. Research has shown that an imbalance in gut bacteria, also known as dysbiosis, can lead to various health issues, including weight gain and metabolic disorders.
The Role of Gut Health in Weight Loss:Latest Discoveries in Microbiome Research
Recent studies have identified specific strains of gut bacteria that are associated with weight loss and improved metabolic health. These findings have opened up new avenues for the development of targeted probiotics and other therapies aimed at modulating the gut microbiome for weight management.
How Gut Health Affects Weight Regulation
Gut health significantly influences weight regulation through various mechanisms, including the modulation of metabolic rate and the extraction of calories from food. An imbalance in gut bacteria can lead to impaired glucose metabolism and increased fat storage, contributing to weight gain.
How Gut Bacteria Influence Metabolism
Gut bacteria play a pivotal role in metabolism, influencing how our bodies extract energy from food and regulate fat storage. Certain bacterial enzymes can enhance calorie extraction, while others may influence metabolic rate and insulin sensitivity.
Bacterial Enzymes and Calorie Extraction
Bacterial enzymes in the gut can break down complex carbohydrates, increasing the amount of calories extracted from food. This process can contribute to weight gain if not balanced by other metabolic processes.
Inflammation and Metabolic Rate
Chronic inflammation, often associated with an imbalance in gut bacteria, can negatively impact metabolic rate, leading to weight gain and metabolic disorders. Maintaining a healthy balance of gut bacteria is crucial for regulating inflammation and supporting metabolic health.
The Gut Microbiome Explained
The gut microbiome, a complex ecosystem within our digestive system, plays a crucial role in our overall health and weight management. It consists of trillions of microorganisms, including bacteria, viruses, and fungi, that live in our gastrointestinal tract. These microbes are not just passive inhabitants; they actively influence our metabolism, immune system, and even brain function.
Diversity of Gut Bacteria and Weight Management
A diverse gut microbiome is essential for maintaining a healthy weight. Research has shown that individuals with a greater variety of gut bacteria tend to have better weight management. This diversity allows for a more robust metabolic system, capable of efficiently processing nutrients and regulating energy balance.
Key Bacterial Species for Weight Control
Certain bacterial species have been identified as key players in weight management. For instance, Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus are known to contribute positively to gut health. These beneficial bacteria help in:
- Enhancing nutrient absorption
- Regulating appetite and satiety signals
- Modulating the immune system to reduce inflammation
Measuring Your Microbiome Health
Understanding the health of your gut microbiome can be achieved through various tests, including stool tests that analyze the genetic material of the microbes present. These tests can provide insights into the diversity and balance of your gut bacteria, helping identify potential issues related to weight management.
Dysbiosis: When Gut Balance Goes Wrong
Dysbiosis occurs when the balance of the gut microbiome is disrupted, leading to a range of health issues, including weight gain and metabolic disorders. Factors contributing to dysbiosis include poor diet, antibiotics, and stress.
Warning Signs of Poor Gut Health
Recognizing the signs of dysbiosis is crucial for early intervention. Common indicators include:
- Bloating and gas
- Irregular bowel movements
- Fatigue and brain fog
- Unintentional weight changes
The Connection to Weight Gain
Dysbiosis can lead to weight gain through several mechanisms, including increased inflammation, impaired nutrient absorption, and altered metabolic signaling. Restoring balance to the gut microbiome is essential for addressing weight-related issues.
Recent Research on Gut Health and Weight Loss
Groundbreaking research in 2023 has shed new light on the intricate mechanisms linking gut microbiota to weight regulation. This new evidence has significant implications for developing effective weight loss strategies.
Breakthrough Studies in 2023
The year 2023 has seen several pivotal studies that advance our understanding of gut health’s role in weight management. These studies have employed cutting-edge techniques to investigate the complex interactions between gut bacteria and host metabolism.
Clinical Trial Results from Major Universities
Recent clinical trials conducted at prestigious institutions have provided compelling evidence for the efficacy of gut-targeted interventions in weight loss. For instance, a study published in a leading scientific journal demonstrated that modulation of gut microbiota through dietary changes resulted in significant weight reduction in obese participants.
New Understanding of Microbiome Manipulation
Researchers have made substantial progress in understanding how to manipulate the gut microbiome for weight management. This includes the use of prebiotics and probiotics to enhance the growth of beneficial bacteria and improve metabolic health.
What Scientists Are Discovering About Gut-Weight Relationships
Scientists are continually uncovering the complex relationships between gut health and weight regulation. Emerging evidence suggests that the composition of gut microbiota plays a crucial role in determining an individual’s weight loss potential.
Personalized Nutrition Based on Gut Profiles
A key area of research involves tailoring dietary recommendations based on an individual’s gut microbiome profile. Studies have shown that personalized nutrition plans can lead to more effective weight loss outcomes by taking into account the unique characteristics of an individual’s gut bacteria.
Future Directions in Gut-Targeted Therapies
Looking ahead, researchers are exploring novel gut-targeted therapies for weight management, including the use of microbiome-based diagnostics to identify individuals at risk of obesity and related metabolic disorders.
Dietary Factors That Shape Your Gut Microbiome
Eating the right foods can foster a healthy gut microbiome, which is essential for effective weight loss and maintenance. The gut microbiome is a complex ecosystem that is influenced by various dietary factors.
Fiber-Rich Foods and Their Impact
Fiber-rich foods are crucial for maintaining a healthy gut microbiome. They act as prebiotics, feeding the beneficial bacteria and promoting their growth.
Top 10 Prebiotic Foods for Gut Health
- Asparagus
- Bananas
- Onions
- Garlic
- Whole Wheat Bread
- Oats
- Apples
- Barley
- Seaweed
- Berries
How Fiber Feeds Beneficial Bacteria
Fiber is fermented by beneficial bacteria in the colon, producing short-chain fatty acids that provide energy to the cells lining the colon and help maintain a healthy gut environment.
Probiotics vs. Prebiotics: What's the Difference?
Probiotics are live bacteria and yeasts that are beneficial for gut health, while prebiotics are non-digestible fibers that feed the beneficial bacteria. Both are essential for maintaining a balanced gut microbiome.
Effective Probiotic Strains for Weight Management
- Lactobacillus acidophilus
- Bifidobacterium bifidum
- Streptococcus thermophilus
Natural Sources vs. Supplements
While probiotics and prebiotics can be obtained through supplements, natural sources such as fermented foods and fiber-rich vegetables are generally more beneficial.
Foods to Avoid for Optimal Gut Health
Certain foods can disrupt the balance of the gut microbiome. It’s essential to limit or avoid these foods to maintain optimal gut health.
Hidden Gut Disruptors in Common Foods
- Processed meats
- Refined sugars
- Artificial sweeteners
Transitioning Away from Harmful Ingredients
Gradually replacing harmful ingredients with healthier alternatives can help restore balance to the gut microbiome. This includes choosing whole foods over processed ones and reading labels carefully.
Habits & Lifestyle Changes for Better Gut Health
A well-functioning gut is heavily influenced by daily habits and lifestyle choices. By making informed decisions about sleep, stress management, and exercise, individuals can significantly improve their gut health.
Sleep Quality and Gut Function
Sleep plays a critical role in maintaining a healthy gut microbiome. Research has shown that poor sleep quality can disrupt the balance of gut bacteria, leading to various health issues.
The Circadian Rhythm-Gut Connection
The body’s internal clock, or circadian rhythm, regulates various physiological processes, including gut function. Irregular sleep patterns can desynchronize this rhythm, negatively impacting gut health.
Sleep Hygiene Practices for Gut Health
To promote better sleep and, consequently, gut health, it’s essential to practice good sleep hygiene. This includes maintaining a consistent sleep schedule, creating a relaxing bedtime routine, and avoiding caffeine and electronics before bedtime.
Stress Management Techniques
Chronic stress can have a detrimental effect on the gut microbiome. Effective stress management is crucial for maintaining gut health.
How Chronic Stress Damages Gut Bacteria
Chronic stress can lead to increased cortisol levels, which can disrupt the balance of gut bacteria and impair the gut barrier function.
Mindfulness Practices for Gut-Brain Balance
Mindfulness practices, such as meditation and deep breathing, can help mitigate stress and promote a healthy gut-brain axis.
Exercise and Its Effect on Gut Bacteria
Regular exercise is known to positively influence the gut microbiome. Different types of exercise can have varying effects on gut bacteria.
Optimal Exercise Types for Microbiome Health
Aerobic exercises, such as running and cycling, have been shown to enhance gut microbiome diversity. Resistance training can also contribute to a healthier gut.
Building a Gut-Friendly Fitness Routine
To maximize the benefits for gut health, it’s recommended to incorporate a mix of aerobic exercise, resistance training, and flexibility exercises into your fitness routine.
| Lifestyle Factor | Impact on Gut Health |
|---|---|
| Sleep Quality | Poor sleep can disrupt gut bacteria balance |
| Stress Management | Chronic stress can damage gut bacteria |
| Exercise | Regular exercise can enhance gut microbiome diversity |
The Gut-Brain Axis and Weight Regulation
The intricate communication network between the gastrointestinal tract and the central nervous system, known as the Gut-Brain Axis, has a profound impact on our weight. This complex system influences various physiological processes, including appetite control, metabolism, and fat storage.
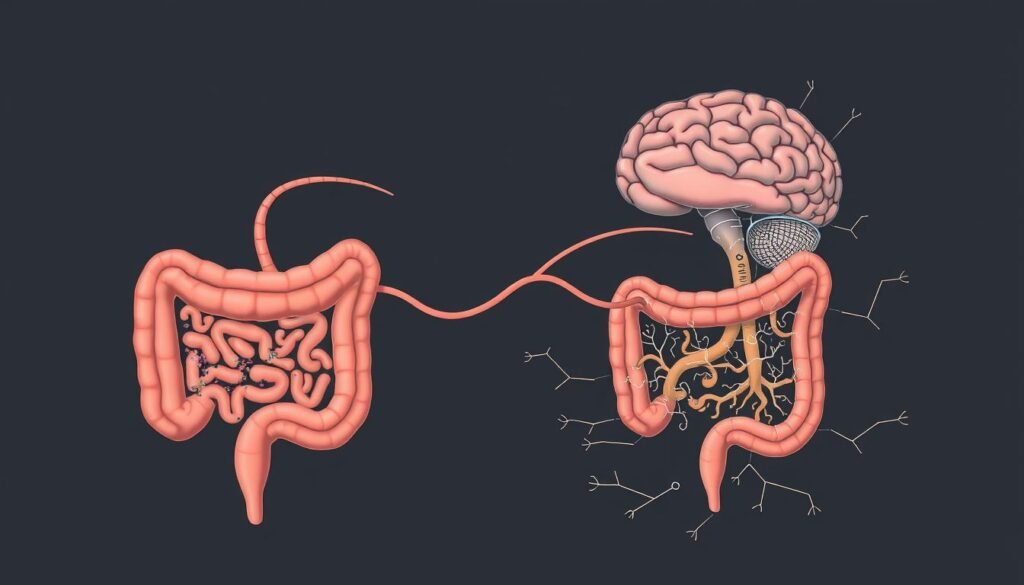
How Your Gut Communicates with Your Brain
The gut and brain communicate through a bidirectional signaling network involving neurotransmitters and the vagus nerve. This communication pathway allows the gut to influence brain functions, including those related to appetite and satiety.
Neurotransmitters Produced in the Gut
The gut produces various neurotransmitters, such as serotonin and dopamine, which play crucial roles in regulating mood, appetite, and metabolism. These chemicals can significantly impact our eating behaviors and weight management.
Vagus Nerve Signaling and Appetite Control
The vagus nerve acts as a key messenger between the gut and the brain, transmitting signals that influence appetite control and satiety. Stimulating the vagus nerve can help regulate eating habits and support weight loss efforts.
Emotional Eating and Gut Health
Emotional eating is closely linked to gut health, with stress and negative emotions often triggering overeating or poor food choices. Understanding this connection is vital for developing effective strategies to manage emotional eating.
Breaking the Stress-Eating Cycle
To break the stress-eating cycle, it’s essential to adopt stress management techniques, such as mindfulness, meditation, or yoga. These practices can help reduce stress-induced eating behaviors and promote a healthier relationship with food.
Gut-Friendly Mood Enhancement Strategies
Incorporating gut-friendly mood enhancement strategies, such as consuming probiotics, prebiotics, and fermented foods, can support both gut health and mental well-being. These approaches can help alleviate symptoms of anxiety and depression, which are often associated with emotional eating.
Practical Steps to Reset Your Gut for Weight Loss
Resetting your gut health is a crucial step towards achieving sustainable weight loss. A well-functioning gut microbiome is essential for effective metabolism, nutrient absorption, and overall well-being.
A 7-Day Gut Health Plan
Implementing a 7-Day Gut Health Plan can help jumpstart your journey to a healthier gut and weight loss. This plan involves dietary changes, lifestyle adjustments, and monitoring your progress.
Daily Menu Suggestions and Recipes
Incorporate gut-friendly foods such as yogurt, leafy greens, and fermented vegetables into your diet. Here’s a sample menu:
- Breakfast: Overnight oats with berries and almond milk
- Lunch: Grilled chicken salad with mixed greens and avocado
- Dinner: Baked salmon with quinoa and steamed broccoli
Lifestyle Adjustments to Implement
In addition to dietary changes, several lifestyle adjustments can support gut health:
- Increase your water intake to at least 8 glasses a day
- Engage in 30 minutes of moderate exercise daily
- Practice stress-reducing techniques such as meditation or deep breathing
Tracking Progress and Adjusting Your Approach
Tracking your progress is vital to understanding how your body responds to the changes you’ve implemented. Monitor your digestive symptoms and weight changes regularly.
Monitoring Digestive Symptoms and Weight Changes
Keep a food and symptom diary to track any changes in your digestive health and weight. Note any improvements or setbacks.
When to Consult a Healthcare Provider
If you experience persistent or severe digestive issues, it’s essential to consult a healthcare provider. They can offer personalized advice and treatment options tailored to your needs.
By following this 7-day plan and making necessary adjustments, you can effectively reset your gut and support your weight loss journey.
Common Gut Health Disruptors in Modern Life
Modern life is filled with factors that can disrupt our gut health, leading to weight gain and other health issues. Our gut microbiome is sensitive to various external and internal factors, and understanding these disruptors is crucial for maintaining a healthy balance.
Antibiotics and Weight Gain
Antibiotics, while lifesaving, can significantly impact our gut health by altering the balance of our microbiome. Research has shown that antibiotic use can lead to weight gain, particularly in children and adolescents.
Protective Strategies During Antibiotic Treatment
To minimize the impact of antibiotics on gut health, consider taking probiotics during and after treatment. Foods rich in fiber can also help support the recovery of your gut microbiome.
Rebuilding Gut Flora After Medication
After completing antibiotic treatment, focus on consuming fermented foods like yogurt, kefir, and sauerkraut to help repopulate your gut with beneficial bacteria.
Ultra-Processed Foods and Gut Inflammation
Ultra-processed foods are another significant disruptor of gut health, often containing additives and preservatives that can cause inflammation. A diet high in processed foods can lead to gut dysbiosis, negatively affecting overall health.
Identifying Hidden Inflammatory Ingredients
When shopping, be aware of ingredients like artificial sweeteners, certain emulsifiers, and excessive salt, which can contribute to gut inflammation. Always read food labels carefully.
Whole Food Alternatives to Processed Products
Opt for whole, unprocessed foods as much as possible. Replace processed snacks with fruits, nuts, and vegetables to reduce your exposure to potentially inflammatory ingredients.
Environmental Factors Affecting Gut Health
Environmental factors, including exposure to certain chemicals, can also disrupt our gut health. Household cleaning products and pesticides have been linked to changes in the gut microbiome.
Household Chemicals and Microbiome Disruption
Some household chemicals can alter the balance of our gut bacteria. Be cautious with the use of antibacterial soaps and cleaning products.
Creating a Gut-Friendly Home Environment
To create a gut-friendly home, opt for natural cleaning products and reduce the use of plastics. Incorporating plants into your home can also help improve indoor air quality.
Conclusion: Nurturing Your Gut for Sustainable Weight Management
Nurturing your gut is crucial for achieving sustainable weight management. By understanding the intricate relationship between gut health and weight loss, you can adopt a more effective approach to your weight loss journey.
A healthy gut microbiome is essential for optimal metabolism, nutrient absorption, and overall well-being. By incorporating dietary factors such as fiber-rich foods, probiotics, and prebiotics, you can promote a balanced gut ecosystem.
Essential habits like maintaining good sleep quality, managing stress, and regular exercise also play a significant role in supporting gut health. By combining these habits with a gut-friendly diet, you can create a robust foundation for sustainable weight management.
By prioritizing gut health and making informed lifestyle choices, you can achieve a healthier, more balanced you. Focus on nurturing your gut, and you’ll be on the path to sustainable weight management and overall wellness.
FAQ
What is the connection between gut health and weight loss?
Gut health plays a crucial role in weight loss as it affects the way the body regulates metabolism, extracts calories, and stores fat. A healthy gut microbiome is essential for optimal weight management.
How do gut bacteria influence metabolism?
Gut bacteria produce enzymes that help extract calories from food, and an imbalance in gut bacteria can lead to changes in metabolic rate, affecting weight regulation.
What are prebiotics and probiotics, and how do they impact gut health?
Prebiotics are non-digestible fibers that feed beneficial bacteria, while probiotics are live bacteria that promote a healthy gut microbiome. Both can help support weight loss and overall gut health.
How can I measure my microbiome health?
Microbiome health can be measured through tests that analyze the diversity and balance of gut bacteria. Consulting a healthcare provider can help determine the best testing options.
What are some common disruptors of gut health in modern life?
Common disruptors include antibiotics, ultra-processed foods, and environmental factors such as household chemicals. Being aware of these disruptors can help individuals take steps to mitigate their impact.
How can I reset my gut for weight loss?
Resetting your gut involves adopting a healthy diet rich in fiber, managing stress, getting quality sleep, and exercising regularly. A 7-day gut health plan can be a good starting point.
What lifestyle changes can I make to support gut health?
Improving sleep quality, practicing stress management techniques, and engaging in regular exercise can all support gut health and contribute to sustainable weight management.
Are there specific foods that can help or harm gut health?
Yes, fiber-rich foods and prebiotic foods can help support gut health, while ultra-processed foods and those containing certain additives can harm it. Being mindful of food choices is crucial.